After a green revolution, there is no doubt that the productivity of the Indian Agri-sector is increased by 10 folds but there are some negative consequences that we are facing today in the form of environmental degradation.
Presently, the 30% of total land area in India is already degraded. Majorly this due to the over cultivation, deforestation, use of chemical fertilizers & pesticides and unsustainable agriculture practices.
Increasing population and rising food demand puts India’s food security under threat. Whereas, degraded land reduces the productivity of the land and releases soil carbon and nitrous oxide into the atmosphere, making one of the most important contributors to climate change.
Therefore, it is become important to restore the land to ensure the food security in India and fight against climate change.
Affected Areas
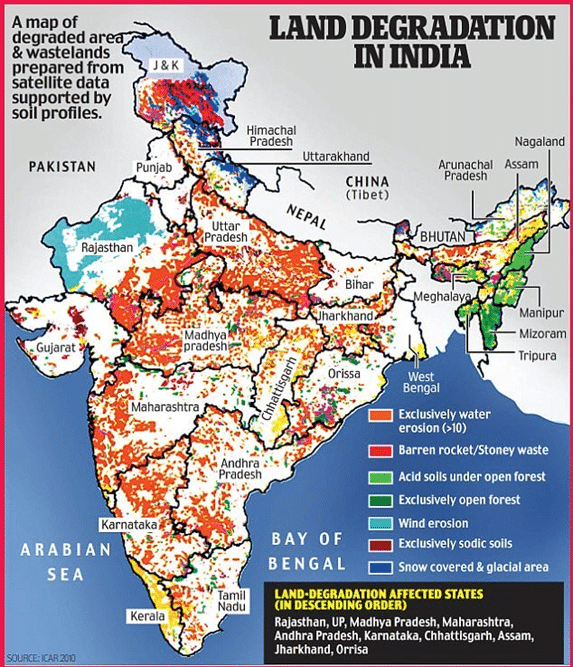
Major part of India is mostly affected by the water and wind erosion. Whereas the Rajasthan is the most affected state in India followed by Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
Impact on food security
It is estimated that India’s demand for food will grow at a rate of two to three percent until 2025, with demand outpacing supply by 2035 – even if productivity increases at its current rate.
In such scenario, India will have two options either increase it’s production capacity or import agriculture produce from the other nations. Importing from other countries will increase the prices in the retail markets and this may become threat to our food security.
Impact on climate Change
The current global food system contributes roughly 25-30 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions. Increasing food demand and reduced productivity will need more land to fulfil food demand and hence, more greenhouse gas emissions are expected.
Degraded land also releases soil carbon and nitrous oxide into the atmosphere, making one of the most important contributors to climate change.
Here’s what needs to done to restore degraded land
Afforestation
Afforestation prevents the soil erosion. India is doing better when it comes to planting more trees. In 2019, the total forest and tree cover in India increased to 24.56 percent.
India has set a new target of 33 percent of its land under forest cover. Therefore, there is still long way to go to achieve the set goals.
Prevent Deforestation
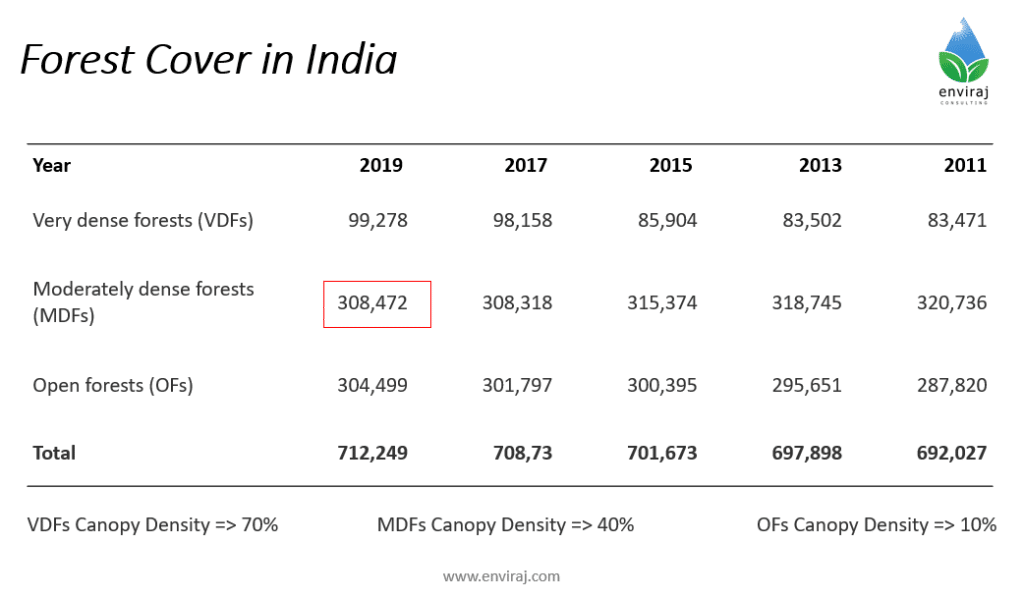
Indian forests are divided into three categories; very dense forests (VDFs), moderately dense forest (MDFs) and Open forests (OFs). In the last decade we have gained overall forest cover but we have lost significant amount of moderately dense forests. These forests are great carbon sinks and covers large part of India.
Therefore, we need to ensure while planting new forests we need to preserve old ones too.
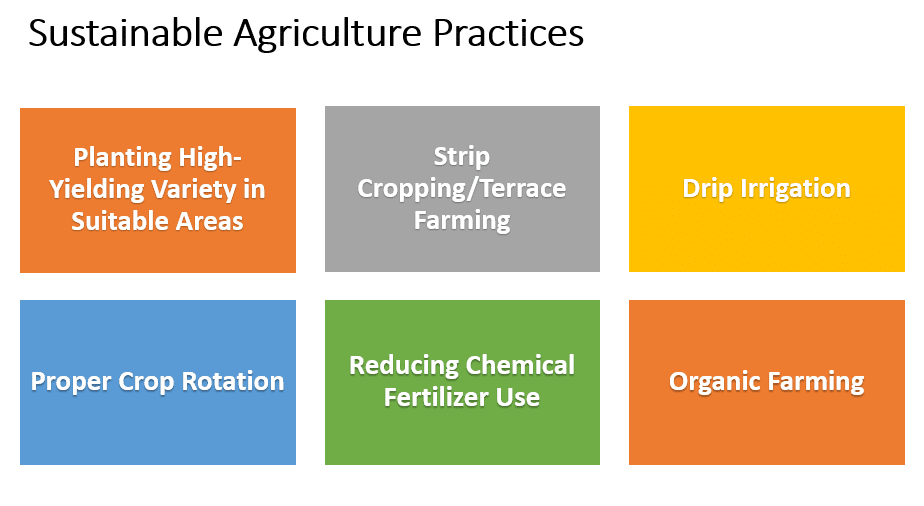
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Expanding food production have often come at a heavy cost to the natural environment. Important key resources like water, soil quality and land are moving in a very unfavourable direction.
Constant use of chemical-based inputs like fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides and mechanized farming have led to overexploitation of natural resources, especially groundwater and soil to the extent that most of the farming enterprises have turned out to be environmentally unsustainable.
Below are the some practices that needs to be adopted for the sustainable agriculture.
Food supply chain management
India waste 30% of the food produced annually through losses that mainly occur during the production, transport and storage stages of the supply chain. Reduction in food waste. Improvement in supply chain would offset food waste and reduce prices for consumers while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving food security.
Management techniques that involve changing diets would allow for a greater variety of crops, less water needed for production and improved nutrition, which would reduce land degradation, food waste and provide more equitable access to food.
Forest fire management
India recorded 82,170 forest fire alerts from April 1-14, 2021 nearly double the number reported during the same period past year, according to Global Forest Watch (GFW), an open-source monitoring application. According to the data, the number of forest fire alerts in April 2021 is also the highest in five years.
Fires are a major cause of forest degradation and have wide ranging adverse ecological, economic and social impacts. Taking into consideration the serious nature of the problem, it is necessary to make some major improvements in the forest fire management strategy for the country.
Conclusion
Land degradation is not only an environmental concern, it has serious impact on food & water security, biodiversity, economy and climate change. India is a land scare country, protecting and restoring land is very important to ensure the sustainable future.

